Training methods in video analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) in video surveillance will continue to gain momentum thanks to rapid technological developments. A status quo.
The term artificial intelligence is often equated - somewhat inflationarily - with many equivalent terms. But what is actually a simple analysis and where does artificial intelligence come in? Whether it's a self-driving car, voice recognition, or an AI-enabled camera, the foundation of any system that makes decisions on its own is data analysis. For example, existing data sets are often scanned for certain patterns in order to make decisions or predict events. An AI makes use of this analysis and makes assumptions on its own. Decisions and predictions are future-based and do not rely solely on existing data. It is important to distinguish between different forms of intelligent analysis.
What does AI actually mean?
Weak AI (called Narrow AI or Artificial Narrow Intelligence [ANI]) is conditioned to perform specific tasks. Weak AI describes a majority of all robust AI applications such as Apple's Siri, Amazon's Alexa or IBM Watson. We speak of so-called strong AI, a theoretical form of AI, if it had intelligence comparable to that of humans. This would then have acquired an actual consciousness, which would be able to solve problems independently and plan events for the future. An artificial superintelligence (ASI) that would surpass the human brain is still of a theoretical nature, but this does not rule out the possibility that researchers are already working on its development. Intelligent video analytics is usually referred to when software-based analytics modules for operation on servers, recorders or in cameras are applied in the automatic detection of security-related objects or events. These enable real-time object detection, object tracking, identification and scene interpretation. Depending on the settings, time, date, focal length and shutter speed can be extracted from the so-called metadata of the video streams. To obtain and extend this pool of aggregated metadata in different scenes and views, an extremely large number of training units of classified scenes and objects are required.
One thing is certain: the use of metadata and technical tools increases the efficiency and reliability of video data analysis enormously. Discrete GPUs (Graphics Processing Unit) of graphics cards today use their own video memory. Algorithms operating directly in the camera use dedicated GPUs conditioned for video analysis. Additional computing power can be provided via various systems. Whether this is via the company's own servers and with its own IT environment (on-premise), via server-based data processing (cloud-based approaches) or via hybrid approaches.
Due to increasing computing power, it will be possible to integrate better and better algorithms over the years. It was thus only a small step to reconstruct three-dimensional scenes from a 2D video image. In the meantime, it is no longer only possible to recognize objects, but also to register further attributes regarding speed, size, direction and behavior of a route in a procedural way. Moore's Law", according to which computing power nearly doubles every 18 months, should continue to help determine increasingly valid objects of interest.
Edge-based analysis
A security camera equipped with analytics not only recognizes a person using deep learning and converts video information into data, but also creates metadata. In practice, the spectrum enables AI to recognize a car, a person, or a bicycle, for example, or to track an entire scene. The more data that is included, the more scenarios can be trained. Humans are currently still quite a bit smarter than deep learning algorithms: In the video domain, training methods require 100,000 to millions of data sets to produce a broadly accurate result. For example, classification is based on different objects such as human, animal, object and camera angle. Current cameras have powerful processors, with which parallel operation in video analysis and encoding of the video data is often possible by a processor of the camera. This is then referred to as edge-based analysis. However, server-based video analysis is currently still considered the most common solution, in which two different system architectures can also be implemented, enabling, for example, multiple analysis modules in parallel operation.
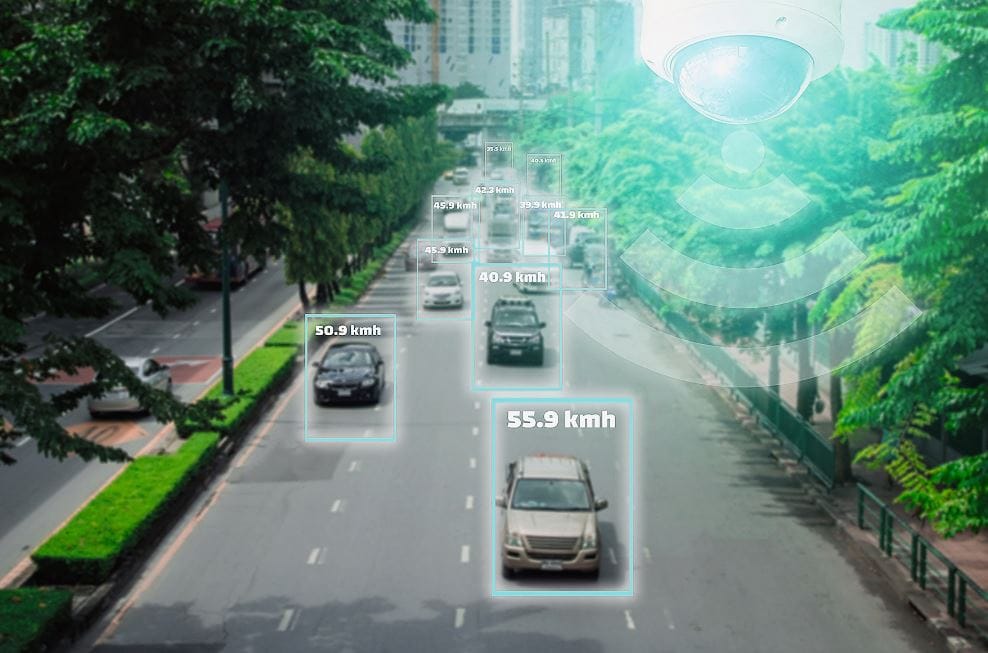

Typical use scenarios of AI in video security systems
The field of application of AI in video security systems opens up a very broad spectrum. It ranges from early fire detection, car license plate recognition, facial recognition, skin temperature analysis and people counting to the prediction of possible thefts (behavioral), accompanied by audio analysis or the observation of traffic incidents. Typical case studies of traffic solutions are based on counting, traffic flow counting, license plate recognition, traffic density and distance. A so-called event detection (ED) system is able to immediately detect all desired events in a tunnel or on an open stretch of road, such as regulations, tunnel ventilation shutdowns, traffic lane closures.
Prerequisites for a successful use of AI in video security technology
The use of the best AI-based products depends on the camera/lens unit and the intended application. Not only the resolution, object quality, but also the viewing distance or angle, the illumination and the tilt angle of an IP camera play a crucial role in surveillance. A good trust of the operator in the supply chain of the AI solution is therefore indispensable. This can be promoted through transparency and regular exchange between operator, installer and manufacturer. Criteria such as the type, origin and scope of the training data provide a clear picture. For example, it can be discussed whether improved algorithms can be retrofitted into the system and whether they can be trained under all conditions (for example, for conditions such as summer/winter, day/night and weather conditions).
Compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is mandatory under all circumstances. Some providers of IP cameras make statements about the accuracy of detection. But what do technical statements of an accuracy of 95 percent mean, for example? Example: If an AI-based facial recognition system is to be used to identify a criminal person, in this case an accuracy of 99.9 percent would still result in a false positive rate of 100 people out of 100,000 faces. Crucial questions in this context are: What error rates are acceptable for the particular application planned? How and under what circumstances did the data accuracies come about? Just as important, however, are the basic specifications of the manufacturers and developers.

AI in video security technology still lacks both industry or normative standards and ethical standards. Therefore, there will still be some learning curves to master in AI-based video security technology. Due to the complexity of the topic, the Swiss Association of Security System Installers (SES Association) advises that, in the sense of a "proof of concept," providers offer a test installation in the object, if possible, to verify whether the operator's expectations can be met by the manufacturer's technology. It should be ensured that exactly the camera and lighting technologies as well as other framework conditions for an optimal use of all equipment can be claimed for the purpose of an application in the test phase.
If multiple AI-based solutions are to be considered, care should be taken to use the same camera signals to feed into the AI in order to understand a true comparison in terms of different conditions such as day/night and weather conditions.
Future possibilities
The spectrum of AI-based solutions will still hold open many exciting developments. In the medium to long term, AI is likely to contribute to a significant reduction in false alarms, which will become particularly important with remote switching of 24/7 control centers and a significant reduction in the burden of centralizing information so that PSAPs can better focus on real alarms without increasing PSAP staff. Also, in general, increased AI camera support will help save tremendous time in forensic evaluations. Minute attributes and specialized search functions for people with the same outerwear, such as blue pants, can lead to extremely fast search results with enormous amounts of data. Even image distortions of extreme wide-angle lenses will one day be a thing of the past thanks to AI-based image correction. Even insects in front of a camera lens will not always necessarily lead to false alarms.
Summary of the document "Artificial Intelligence in Video Security Technology" from the Swiss Association of Security System Installers (SES) (to be published soon) and the German BHE Association.