Going on vacation by car: These rules apply - this equipment is mandatory
Before you set off on vacation this summer, you should completely check your vehicle to ensure that you can travel legally and safely through Europe. The prescribed equipment and the conditions for driving on the roads - whether toll-free or subject to tolls - vary from country to country.

Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to fines or impair safety while driving. For this reason, the Touring Club Switzerland (TCS) provides drivers with a map showing the relevant regulations in the individual countries. The TCS also recommends a vehicle check before departure to avoid breakdowns, especially during the busy summer travel season.
CH stickers, warning triangles and safety vest
When traveling through Europe by car, every driver must carry certain items with them. At the top of the list is the CH sticker, which must be affixed to the rear of the vehicle. This often neglected label is mandatory throughout Europe; failure to do so can result in a fine. The warning triangle must also always be carried. It is mandatory in Switzerland and is also required or recommended in most European countries. It is strongly advised to keep it handy in the trunk so that it is immediately to hand in an emergency. Finally, the safety vest is recommended in many countries in accordance with the EN 471 standard. Although it is not obligatory everywhere - especially not in the Netherlands, Great Britain, Ireland, Greece and the Scandinavian countries - it is still compulsory in most European countries.
Child seats and anti-glare stickers
As in Switzerland, children in most European countries must be strapped into child seats that are appropriate for their size and age. This is mandatory up to a height of 150 cm or an age of 12 years. As each country may have its own regulations, TCS recommends adhering to the Swiss regulations, as these are stricter than in most countries. When traveling to Great Britain or Ireland, headlight dipped beam stickers are essential due to the left-hand traffic. They prevent other road users from being dazzled. In the Balkan countries, it is strongly recommended that you carry spare bulbs with you, with the exception of vehicles with xenon or LED headlights. These are mandatory in Andorra, Croatia and Montenegro and are recommended in France and Macedonia. Finally, the use of daytime running lights or dipped headlights is mandatory - or strongly recommended - in almost all European countries, both during the day and at night.
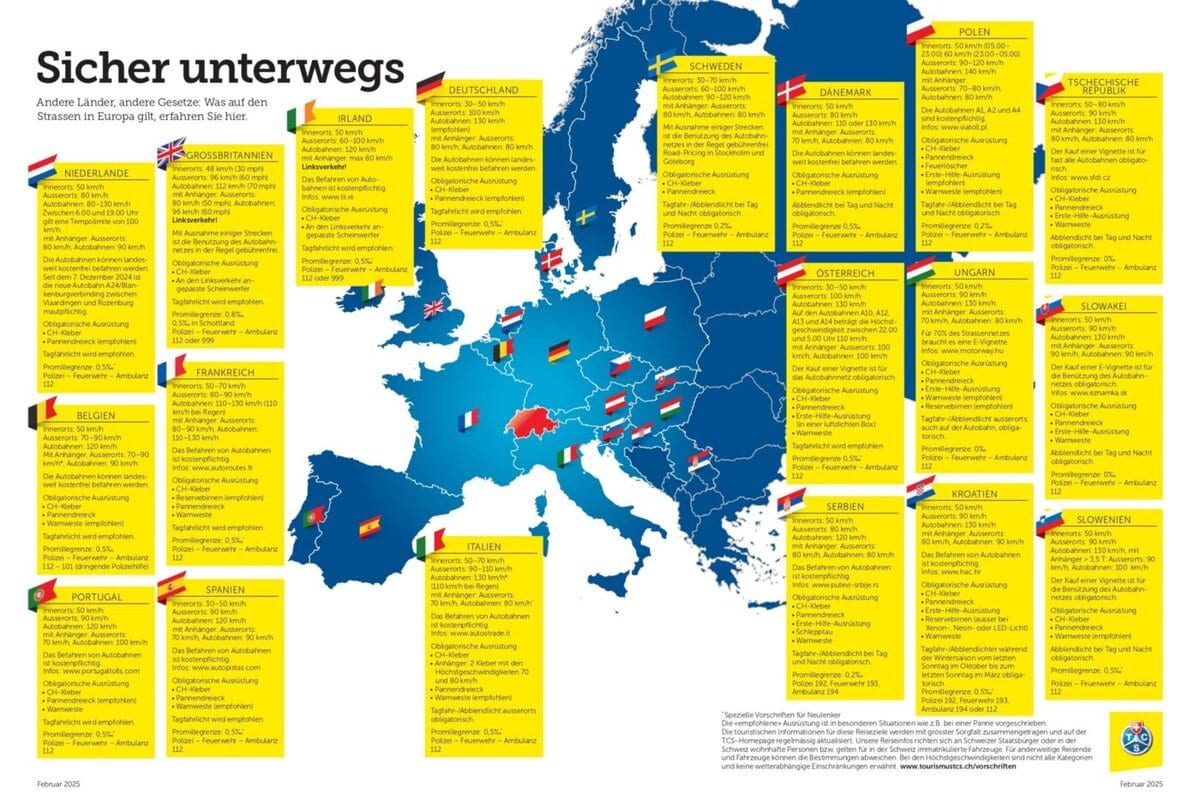
Environmental badge and first aid kit
In several European countries, access to certain urban areas is restricted. An environmental badge may be required to drive in these areas. This is the case in some cities in Belgium, Denmark, Germany, France, the Netherlands, Austria, Spain, the Czech Republic and the United Kingdom. A first aid kit is strongly recommended in many countries. However, it is mandatory in Serbia, Hungary, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Austria. Please note that in Austria it must be kept in a closed, sturdy container.
Wild camping prohibited
Caravans and motorhomes are subject to the same traffic regulations as passenger cars, but their use is governed by special regulations. In Switzerland, for example, a category BE driving license - or C or D if applicable - is required if the total weight of the vehicle (including trailer) exceeds 3500 kg. In Europe, these vehicles are also subject to special regulations, which vary from country to country. It is important to note that wild camping is generally prohibited throughout Europe - with the exception of some countries such as Scandinavia and the Baltic States as well as Scotland, Albania, Moldova and Romania, provided certain conditions are met. Finally, strict regulations often apply to the parking of motorhomes and caravans. It is therefore recommended that you find out about the local regulations before setting off.
Toll highways in some countries
In Germany, Denmark, Sweden, Belgium, Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and the UK, use of the road network is free of charge, with some exceptions for certain tunnels, bridges, special sections or urban areas. In other countries, the purchase of a vignette, either in the form of a sticker or a digital vignette, is required to drive on the highways. This applies in particular to Austria, Slovakia, Slovenia and Hungary. The price depends on the period of validity and the vignette can be purchased online, at petrol stations or at border crossings. In Austria, certain parts of the network are exempt from the vignette requirement, but some tunnels or certain sections are subject to a separate toll.
Different payment methods for toll charges
In France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Croatia and Greece, the highway network is mainly operated with a toll system whose fees vary depending on the section traveled and vehicle class. Payment can be made in cash, by credit card or via electronic payment systems such as Télépéage in France, Telepass in Italy, VIA-T in Spain or Easy Toll and Toll Card in Portugal. The free-flow system without physical barriers is used on some sections: License plates are scanned automatically and payment must then be made online or via a special subscription. Fines can be imposed for non-payment.
Source: TCS









