How fraudsters forge Internet addresses
The National Center for Cybersecurity (NCSC) warns about the pitfalls of fake Internet addresses and recalls the identifying characteristics of an authentic URL.

Last week, the NCSC recorded according to own data a somewhat lower reporting rate, but in one classified ad scam, for example, the Internet address of a payment service was elaborately forged. Many scams are based on spoofing the URL. The NCSC recalls that a URL usually consists of a subdomain ("www"), a domain (e.g., name of the company), and a top level domain (e.g., "ch").
However, during a classified ad scam, the NCSC had become aware of an elaborately designed scam website. To ensure that a link to a fake website was not immediately recognizable as a fake, the fraudsters reserved their own domain, which followed the scheme ".ch-123xyz.com". The reserved domain was extended by the name of the legitimate company, so that the URL presented itself as follows: "www.abcdefgh123.ch-123xyz.com".
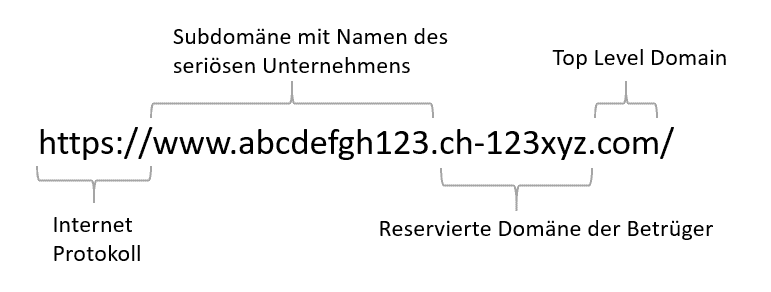
While the difference from the fake URL should be noticeable, at first glance the fraud may not be immediately obvious.
In case of doubt, the actual URL should therefore always be entered in the browser.









